| Safe Haskell | None |
|---|---|
| Language | Haskell98 |
Quantum.Synthesis.GridSynth
Contents
Description
This module implements the approximate single-qubit synthesis algorithm of
- N. J. Ross and P. Selinger, "Optimal ancilla-free Clifford+T approximation of z-rotations". http://arxiv.org/abs/1403.2975.
The algorithm is near-optimal in the following sense: it produces an operator whose expected T-count exceeds the T-count of the second-to-optimal solution to the approximate synthesis problem by at most O(log(log(1/ε))).
- gridsynth :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> U2 DOmega
- gridsynth_gates :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> [Gate]
- data DStatus
- gridsynth_stats :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)])
- gridsynth_phase_stats :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)])
- epsilon_region :: (Floating r, Ord r, RootHalfRing r, Quadratic QRootTwo r) => r -> r -> ConvexSet r
- epsilon_region_scaled :: (Floating r, Ord r, RootHalfRing r, Quadratic QRootTwo r) => DRootTwo -> r -> r -> ConvexSet r
- gridsynth_internal :: forall r g. (RootHalfRing r, Ord r, Floating r, Adjoint r, Floor r, RealFrac r, Quadratic QRootTwo r, RandomGen g) => g -> r -> r -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)])
- gridsynth_phase_internal :: forall r g. (RootHalfRing r, Ord r, Floating r, Adjoint r, Floor r, RealFrac r, Quadratic QRootTwo r, Quadratic r r, RandomGen g) => g -> r -> r -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)])
- mergeBy :: (a -> a -> Ordering) -> [a] -> [a] -> [a]
- first :: (a, b, c) -> a
Approximate synthesis
User-friendly functions
gridsynth :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> U2 DOmega Source #
Output a unitary operator in the Clifford+T group that
approximates Rsub /z/ = e−iθZ/2 to within ε in the
operator norm. This operator can then be converted to a list of
gates with to_gates.
The parameters are:
- a source of randomness g;
- the angle θ;
- the precision b ≥ 0 in bits, such that ε = 2-b;
- an integer that determines the amount of "effort" to put into factoring. A larger number means more time spent on factoring. A good default for this is 25.
Note: the argument theta is given as a symbolic real number. It
will automatically be expanded to as many digits as are necessary
for the internal calculation. In this way, the caller can specify,
e.g., an angle of pi/128 :: SymReal, without having to worry
about how many digits of π to specify.
gridsynth_gates :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> [Gate] Source #
A version of gridsynth that returns a list of gates instead of a
matrix.
Note: the list of gates will be returned in right-to-left order, i.e., as in the mathematical notation for matrix multiplication. This is the opposite of the quantum circuit notation.
gridsynth_stats :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)]) Source #
gridsynth_phase_stats :: RandomGen g => g -> Double -> SymReal -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)]) Source #
A version of gridsynth_stats that returns the optimal operator
up to a global phase. (The default behavior is to return the
optimal operator exactly).
Implementation details
The ε-region
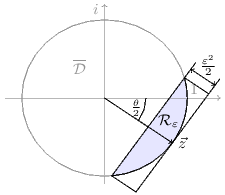
epsilon_region :: (Floating r, Ord r, RootHalfRing r, Quadratic QRootTwo r) => r -> r -> ConvexSet r Source #
The ε-region for given ε and θ is a convex subset of the closed
unit disk, given by
epsilon_region_scaled :: (Floating r, Ord r, RootHalfRing r, Quadratic QRootTwo r) => DRootTwo -> r -> r -> ConvexSet r Source #
The ε-region, scaled by an additional factor of √s, where s > 0. The center of scaling is the origin.
Main algorithm implementation
gridsynth_internal :: forall r g. (RootHalfRing r, Ord r, Floating r, Adjoint r, Floor r, RealFrac r, Quadratic QRootTwo r, RandomGen g) => g -> r -> r -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)]) Source #
The internal implementation of the ellipse-based approximate synthesis algorithm. The parameters are a source of randomness g, the angle θ, the precision b ≥ 0 in bits, and an amount of "effort" to put into factoring.
The outputs are a unitary operator in the Clifford+T group that
approximates Rsub /z/ to within ε in the operator norm;
log0.5 of the actual error, or Nothing if the error is 0;
and the number of candidates tried.
Note: the parameter θ must be of a real number type that has enough
precision to perform intermediate calculations; this typically
requires precision O(ε2). A more user-friendly function that
selects the required precision automatically is gridsynth.
gridsynth_phase_internal :: forall r g. (RootHalfRing r, Ord r, Floating r, Adjoint r, Floor r, RealFrac r, Quadratic QRootTwo r, Quadratic r r, RandomGen g) => g -> r -> r -> Int -> (U2 DOmega, Maybe Double, [(DOmega, Integer, DStatus)]) Source #
The internal implementation of the ellipse-based approximate
synthesis algorithm, up to a phase. The parameters are the same as
for gridsynth_internal.